Main Page: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "thumb|centre|Currently under construction") |
|||
| (148 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | <div align="right">'''Please check [[The first twelve steps on aiCAMstir|the first twelve steps on aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup>]], if you want to create an account as a participant'''</div> | ||
[[File:AiCAMstir™ Trademark Icon, © Stephan Kallee, AluStir, CC-BY-SA 4.0.png|thumb|alt=aiCAMstir logo|The aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> project investigates Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing of Friction Stir Welds]] | |||
The '''aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> project''' investigates '''Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing of Friction Stir Welds.''' | |||
== aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup>: Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing of Friction Stir Welds == | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Computional Fluid Dynamics will be used for optimising the tool design of aiCAMstir tools for lap welding © Mike Lewis and Simon Smith, OxCAM, CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg|thumb|upright=4.5|centre|alt=CFD Analyis showing the material flow caused by a cylindrical FSW tool with coarse threats in a lap joint|Computional Fluid Dynamics will be used for optimising the tool design of aiCAMstir tools for lap welding.<ref name="LewisAndSmith">Mike Lewis and Simon D. Smith: [https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-030-65265-4_15 ''The Development of FSW Process Modelling for Use by Process Engineers.''] In: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society 2021: Friction Stir Welding and Processing XI. 17 February 2021. </ref> The tool is slightly tilted and moves from right to left.]] | |||
|} | |||
It is difficult to choose and optimise the '''friction stir welding''' tool design and welding parameters for '''lap welding''', as shown by many publications.<ref>Matthew Champagne (University of New Orleans): [https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Investigation-of-2195-and-2219-Post-Weld-Heat-for-Champagne/f45e434381add609c50444d60261e6f8e830372f?p2df ''Investigation of 2195 and 2219 Post Weld Heat Treatments for Additive Friction Stir Lap Welds.''] Pages 9, 20-21.</ref> | |||
Thus, the aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> project has been set-up with the objective to add a new '''aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> computer aided manufacturing''' control system to FSW machines, which recommends (or even automatically optimises) parameters based on '''computational fluid dynamics (CFD), analytical models of the [[FSW Power|FSW power]], finite element analysis (FEA), design of experiments (DOE), Wikipedia-like open source cloud data''' and '''artificial intelligence (AI)''' including '''machine learning'''. | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Conventinal butt welding tool used for lap joints at 1200 rpm at 250 mm per min, © Egoitz Aldanondo, Javier Vivas, Pedro Álvarez (LORTEK) and Iñaki Hurtado (MU-ENG), CC BY 4.0.webp|thumb|upright=1.53|centre|alt=The regions of an lap weld made by FSW, e.g. Weld Nugget (WN), Thermo-Mechanically Affected Zone (TMAZ), Advancing Side (ADV) and Retreating Side (RET)|Benchmark: Conventional butt welding tool used for lap joints at 1200 rpm at 250 mm/min<ref name="Aldanondo">Egoitz Aldanondo, Javier Vivas, Pedro Álvarez (LORTEK) and Iñaki Hurtado (MU-ENG): [https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4701/10/7/872 ''Effect of Tool Geometry and Welding Parameters on Friction Stir Welded Lap Joint Formation with AA2099-T83 and AA2060-T8E30 Aluminium Alloys.''] Metals 2020, 10(7), 872, [http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ CC BY 4.0].</ref>]] || [[ File:Computational fluid dynamics analysis of material flow using a conventional friction stir welding tool © Mike Lewis and Simon Smith, OxCAM, CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg|thumb|upright=1.47|centre|Computational fluid dynamics analysis of material flow using a conventional butt welding tool<ref name="LewisAndSmith"/>]] | |||
|} | |||
[[File:Benchmark - Conventinal butt welding tool used for lap joints causing hooking and thinning © Stephan Kallee, AluStir, CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg|thumb|left|alt=Drawing of a conical "Triflat" butt welding tool producing a lap joint|Benchmark: Conventional butt welding tool used for lap joints causing hooking and thinning]] | |||
This international collaborative project will be conducted for producing the next generation of lap welding tools, which overcome the '''problems caused by thinning and hooking'''. A new set of tools will be evaluated and optimised by computational fluid dynamics regarding material flow. | |||
The industrially funded project will be sponsored by a number of industrial companies from various industry sectors and leading '''universities and R&D organsations'''. | |||
{| | |||
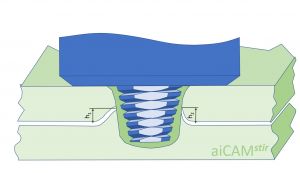
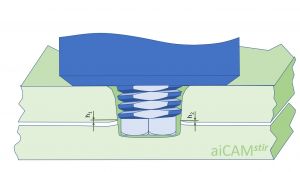
| [[File:Pentagonal aiCAMstir tool for disrupting the oxide layer during lap welding © Stephan Kallee, AluStir CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg |thumb|centre|alt=The tool pin has two regions: Coarse threads in the upper sheet and pentagonal in the joint region between the overlapping sheets|Pentagonal aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> tool for disrupting the oxide layer during lap welding<ref>Marc J. Brooker, A. J. M. (Ton) van Deudekom, Stephan W. Kallee and Peter D. Sketchley: [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/2001ESASP.468..507B ''Applying Friction Stir Welding to the Ariane 5 Main Motor Thrust Frame.''] In: European Space Agency – Publications - ESA SP; 468; 507-512; 2000. ISSN: 0379-6566.</ref><ref>Stephan W. Kallee, E. Dave Nicholas and Wayne M. Thomas: [https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/published-papers/industrialisation-of-friction-stir-welding-for-aerospace-structures-december-2001 ''Industrialisation of friction stir welding or aerospace structures.''] Paper presented at Structures and Technologies - Challenges for Future Launchers, Third European Conference, Strasbourg, 11-14 December 2001.</ref>]] || [[File:Counterflow aiCAMstir tool with left-handed, right-handed and neutral threads on 3 ridges © Stephan Kallee, AluStir, CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg|thumb|centre|alt=The tool pin has has threads that move the plasticised material upwards or downwards and around the pin|Counterflow aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> tool with left-handed, right-handed and neutral threads on 3 ridges<ref name="Aldanondo"/>]] || [[ File:Cylindrical aiCAMstir tool with three rifeled prongs to disrupt the oxide layer © Stephan Kallee, AluStir, CC-BY-SA 4.0.jpg |thumb|centre|Cylindrical aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> tool with three rifeled prongs to disrupt the oxide layer<ref>Wayne M. Thomas, David G. Staines, Ian M. Norris and Ruis de Frias: [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wayne-Thomas-9/publication/273057191_Friction_Stir_Welding_-Tools_and_developments/links/54f5a5c60cf2ba6150679aab/Friction-Stir-Welding-Tools-and-developments.pdf ''Friction Stir Welding –Tools and developments.''] FSW seminar, IST-Porto, Portugal. 3 December 2002.</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
== Project Steering Group == | |||
The participants of the aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> '''Project Steering Group''' will collaborate on ''Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing by Friction Stir Welding'' and will meet in on-line meetings. | |||
* The participants may present their results and provide information about their services and products on the Creative Commons licenced Open Access on the “aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Cloud” | |||
* Industrial companies will pay a participation fee and need to pay for experimental studies. Some of the non-confidential data of their studies and some data of the users of the system will be fed into the open source cloud of the aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> system. | |||
* R&D companies and universities may participate free of charge in the aiCAMstir project, if they get invited and if they get re-elected after continuously feeding the “aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Cloud” with useful data. | |||
* Virtual Awards will be presented to those project participants who make the best contributions. | |||
== Confidentiality == | |||
There will be three levels of confidentiality: Open Access, Project Steering Group only and One-to-One only. In the latter case the tool designs and welding results may be shared with the Project Steering Group, but the tool and workpiece material specifications and workpiece geometry may be kept confidential, e.g. a 5 mm thick 6000 series extrusion was lap welded to a 4xx.x series aluminium casting. | |||
== Founding Partners == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
<!--|+ Caption text --> | |||
|- | |||
! AluStir !! FTS Engineering Answers Ltd !! Transforming Stress Ltd | |||
|- | |||
| Stephan Kallee || Mike Lewis || Simon Smith | |||
|- | |||
| Im Unterdorf 19 <br/> 63826 Geiselbach, Germany || 146 London Road <br/> Biggleswade SG18 8EH, UK || The Sycamores, 43 Kneesworth St <br/> Royston SG8 5AB, UK | |||
|- | |||
| Tel: +49 (0) 6024 6360123 || Tel: +44 (0) 7758 742358 || Tel: +44 (0) 7742 793848 | |||
|- | |||
| [mailto:stephan.kallee@alustir.com stephan.kallee@alustir.com] || [mailto:info@fts-engineeringanswers.com info@fts-engineeringanswers.com] || [mailto:contact@transformstress.co.uk contact@transformstress.co.uk] | |||
|- | |||
| [https://www.alustir.com/ www.alustir.com] || [https://www.fts-engineeringanswers.com/ www.fts-engineeringanswers.com] || [https://www.transformstress.co.uk/ www.transformstress.co.uk] | |||
|} | |||
== Links to new and improved pages == | |||
{| width=100% cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" valign="top" | |||
|- | |||
|style="background:#E5EDDE; border:1px solid #D5DECD"|[[Special:NewPages| | |||
* '''Automatically updated list''' ]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background:#F6FCEF; padding:2px 1px" | | |||
* '''Manually updated list (including significant improvements of existing pages):''' | |||
** '''[[Upcoming events#9th aiCAMstir meeting|Agenda of the 9<sup>th</sup> aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> online meeting''']], ''date to be determined'' | |||
** '''[[Eighth aiCAMstir Meeting, 25 May 2023|Minutes and recording of Eighth aiCAMstir Meeting, 25 May 2023]]''' | |||
** [[Server and software#Software_update|Software update]] including shorter URLs | |||
** [[Seventh aiCAMstir Meeting, 26 January 2023|Seventh aiCAMstir Meeting, 26 January 2023]] | |||
** [[Sixth aiCAMstir Meeting, 20 October 2022]] | |||
** [[Papers presented at the 'Joint International Symposium on Friction Stir Welding and Processsing']], 28-30 September 2022, Leuphana University Lüneburg | |||
** [[Geometrical features analysis by image processing]] | |||
** [[Fifth aiCAMstir Meeting, 9 June 2022]] | |||
** [[Vision#Potential_users_of_the_aiCAMstir_system|Potential users of the aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> system]] | |||
** [[Fourth aiCAMstir Meeting, 10 March 2022|Fourth aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Meeting, 10 March 2022]] | |||
** [[Vision#Automated_shearography|Automated shearography]] | |||
** [[Surface morphology]] | |||
** [[Third aiCAMstir Meeting, 2 December 2021|Third aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Meeting, 2 December 2021]] | |||
** [[Vision#Non-destructive testing concept for automatic examination by LRUT, PAUT_or_X-ray|Concept for in-process LRUT or film-free X-ray examination during FSW with adaptive control of the process parameters]] | |||
** [[Second aiCAMstir Meeting, 30 September 2021|Second aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Meeting, 30 September 2021]] | |||
** [[AiCAMstir Kick-off Meeting, 29 July 2021|aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup> Kick-off Meeting, 29 July 2021]] | |||
** [[LAMEF]] | |||
** [[FTS Engineering Answers Ltd|FTS Engineering Answers]] | |||
** [[Sabe Technology Ltd|Sabe Technology]] | |||
** [[Two companies - one team: Smart Industry Group and Latrock GmbH|Two companies - one team: SIG and Latrock]] | |||
** [[ FSW Power]] | |||
** [[Transforming Stress Ltd|Transforming Stress]] | |||
|} | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Frequently asked questions]] | |||
* [[Vision|The vision]] | |||
* [[The first twelve steps on aiCAMstir|The first twelve steps on aiCAM<sup>''stir''</sup>]] | |||
* [[FSW Power|FSW power]] | |||
* [[Data to be processed]] | |||
* [[Project participants]] | |||
** [[AluStir]] | |||
** [[FTS Engineering Answers Ltd|FTS Engineering Answers]] | |||
** [[LAMEF]] | |||
** [[User:Muhammad Shariq Hasnain|Muhammad Shariq Hasnain]] | |||
** [[Transforming Stress Ltd]] | |||
** [[Sabe Technology Ltd]] | |||
** [[Two companies - one team: Smart Industry Group and Latrock GmbH]] | |||
* [[Literature]] related to the topics of this project | |||
* [[Server and software]] | |||
* [[Upcoming events]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 17 August 2023
The aiCAMstir project investigates Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing of Friction Stir Welds.
aiCAMstir: Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing of Friction Stir Welds
 Computional Fluid Dynamics will be used for optimising the tool design of aiCAMstir tools for lap welding.[1] The tool is slightly tilted and moves from right to left. |
It is difficult to choose and optimise the friction stir welding tool design and welding parameters for lap welding, as shown by many publications.[2]
Thus, the aiCAMstir project has been set-up with the objective to add a new aiCAMstir computer aided manufacturing control system to FSW machines, which recommends (or even automatically optimises) parameters based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD), analytical models of the FSW power, finite element analysis (FEA), design of experiments (DOE), Wikipedia-like open source cloud data and artificial intelligence (AI) including machine learning.
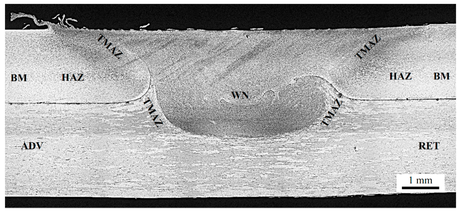 Benchmark: Conventional butt welding tool used for lap joints at 1200 rpm at 250 mm/min[3] |
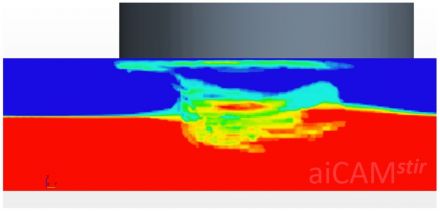 Computational fluid dynamics analysis of material flow using a conventional butt welding tool[1] |
This international collaborative project will be conducted for producing the next generation of lap welding tools, which overcome the problems caused by thinning and hooking. A new set of tools will be evaluated and optimised by computational fluid dynamics regarding material flow.
The industrially funded project will be sponsored by a number of industrial companies from various industry sectors and leading universities and R&D organsations.
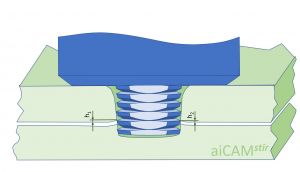 Counterflow aiCAMstir tool with left-handed, right-handed and neutral threads on 3 ridges[3] |
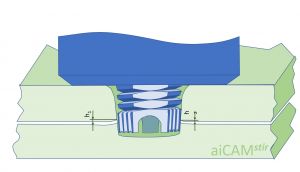 Cylindrical aiCAMstir tool with three rifeled prongs to disrupt the oxide layer[6] |
Project Steering Group
The participants of the aiCAMstir Project Steering Group will collaborate on Artificial Intelligence based Computer Aided Manufacturing by Friction Stir Welding and will meet in on-line meetings.
- The participants may present their results and provide information about their services and products on the Creative Commons licenced Open Access on the “aiCAMstir Cloud”
- Industrial companies will pay a participation fee and need to pay for experimental studies. Some of the non-confidential data of their studies and some data of the users of the system will be fed into the open source cloud of the aiCAMstir system.
- R&D companies and universities may participate free of charge in the aiCAMstir project, if they get invited and if they get re-elected after continuously feeding the “aiCAMstir Cloud” with useful data.
- Virtual Awards will be presented to those project participants who make the best contributions.
Confidentiality
There will be three levels of confidentiality: Open Access, Project Steering Group only and One-to-One only. In the latter case the tool designs and welding results may be shared with the Project Steering Group, but the tool and workpiece material specifications and workpiece geometry may be kept confidential, e.g. a 5 mm thick 6000 series extrusion was lap welded to a 4xx.x series aluminium casting.
Founding Partners
| AluStir | FTS Engineering Answers Ltd | Transforming Stress Ltd |
|---|---|---|
| Stephan Kallee | Mike Lewis | Simon Smith |
| Im Unterdorf 19 63826 Geiselbach, Germany |
146 London Road Biggleswade SG18 8EH, UK |
The Sycamores, 43 Kneesworth St Royston SG8 5AB, UK |
| Tel: +49 (0) 6024 6360123 | Tel: +44 (0) 7758 742358 | Tel: +44 (0) 7742 793848 |
| stephan.kallee@alustir.com | info@fts-engineeringanswers.com | contact@transformstress.co.uk |
| www.alustir.com | www.fts-engineeringanswers.com | www.transformstress.co.uk |
Links to new and improved pages
See also
- Frequently asked questions
- The vision
- The first twelve steps on aiCAMstir
- FSW power
- Data to be processed
- Project participants
- Literature related to the topics of this project
- Server and software
- Upcoming events
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mike Lewis and Simon D. Smith: The Development of FSW Process Modelling for Use by Process Engineers. In: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society 2021: Friction Stir Welding and Processing XI. 17 February 2021.
- ↑ Matthew Champagne (University of New Orleans): Investigation of 2195 and 2219 Post Weld Heat Treatments for Additive Friction Stir Lap Welds. Pages 9, 20-21.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Egoitz Aldanondo, Javier Vivas, Pedro Álvarez (LORTEK) and Iñaki Hurtado (MU-ENG): Effect of Tool Geometry and Welding Parameters on Friction Stir Welded Lap Joint Formation with AA2099-T83 and AA2060-T8E30 Aluminium Alloys. Metals 2020, 10(7), 872, CC BY 4.0.
- ↑ Marc J. Brooker, A. J. M. (Ton) van Deudekom, Stephan W. Kallee and Peter D. Sketchley: Applying Friction Stir Welding to the Ariane 5 Main Motor Thrust Frame. In: European Space Agency – Publications - ESA SP; 468; 507-512; 2000. ISSN: 0379-6566.
- ↑ Stephan W. Kallee, E. Dave Nicholas and Wayne M. Thomas: Industrialisation of friction stir welding or aerospace structures. Paper presented at Structures and Technologies - Challenges for Future Launchers, Third European Conference, Strasbourg, 11-14 December 2001.
- ↑ Wayne M. Thomas, David G. Staines, Ian M. Norris and Ruis de Frias: Friction Stir Welding –Tools and developments. FSW seminar, IST-Porto, Portugal. 3 December 2002.