Data to be processed: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
* Reduce the reaction time | * Reduce the reaction time | ||
* Automate the documentation | * Automate the documentation | ||
* Provide more attractive products and services<ref name="FEF">Marion Purrio and Guido Buchholz ([http://www.fef-aachen.de/contact.html FEF Forschungs- und Entwicklungsgesellschaft Fügetechnik GmbH])[Webinar: Vorgehensweise bei Digitalisierungsprojekten in der Schweißtechnik.] 29 April 2021.</ref> | * Provide more attractive products and services<ref name="FEF">Marion Purrio and Guido Buchholz ([http://www.fef-aachen.de/contact.html FEF Forschungs- und Entwicklungsgesellschaft Fügetechnik GmbH])[https://www.linkedin.com/events/digitalisierunginderschwei-tech6777958989893304320/ ''Webinar: Vorgehensweise bei Digitalisierungsprojekten in der Schweißtechnik.''] 29 April 2021.</ref> | ||
=== Traps === | === Traps === | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
* Humans need to be involved | * Humans need to be involved | ||
* Raw data aren't providing information | * Raw data aren't providing information | ||
* ''Visual management'' is required | * ''Visual management'' is required<ref name="FEF" /> | ||
Revision as of 07:50, 30 April 2021
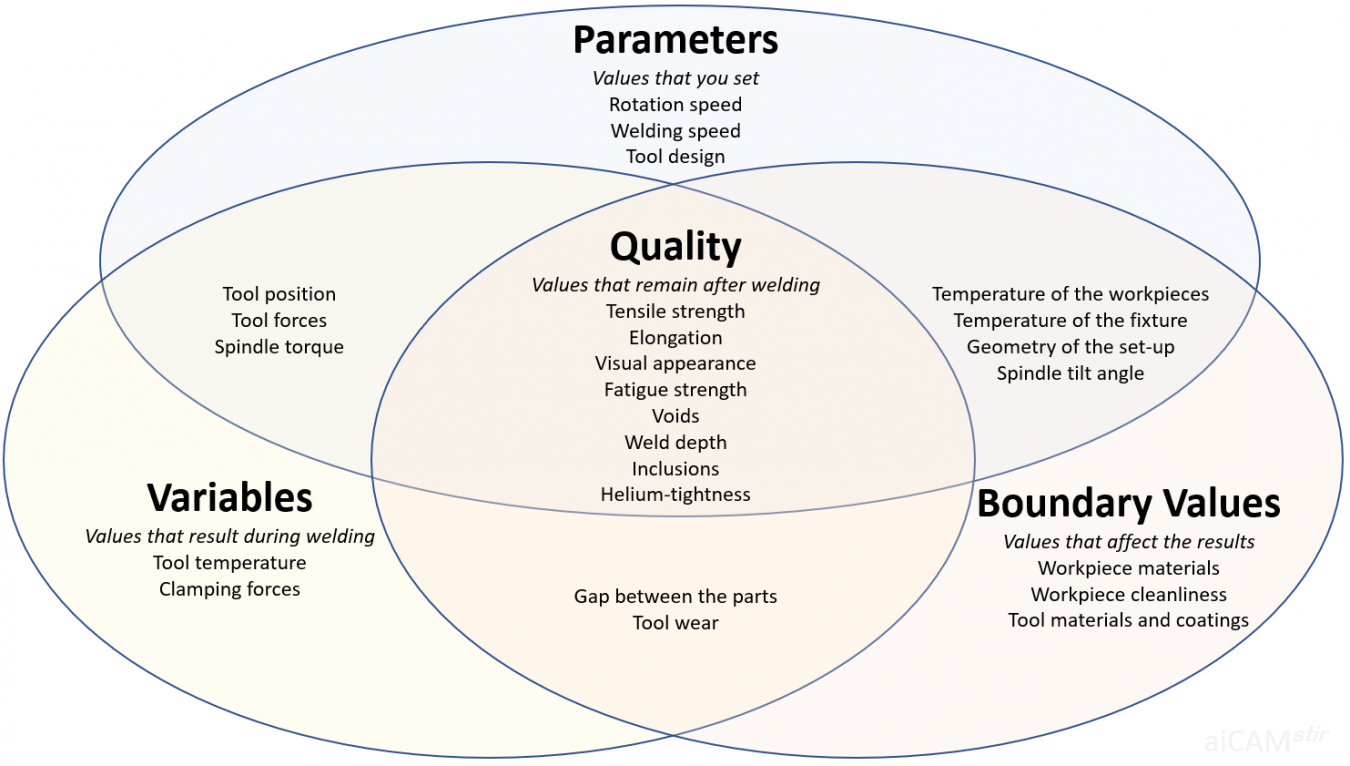
Data to be processed in the aiCAMstir project are parameters, variables, boundary values and quality.
Key data to be processed
According to digitalisation and data processing experts, the following categorisation of key data could be considered:
| Parameters | Variables | Boundry Values | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Values that you set | Values that result during welding | Values that affect the results | Quality |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|||
The categorisation depends on the concept and complexity of the machine. Modern FSW machines provide close-loop force and position control algorithms, which complicate the distinction between parameters and variables. Some machines use the temperature as a parameter that can be set, e.g. to change the parameters if the tool gets too hot.
Please feel free to improve the classification above or to propose an alternative classification. Or use the discussion page for discussing changes.
CAM and FSW
- Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) includes data monitoring, data processing and data visualisation
- Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is a special process, and its quality can only be determined statistically
Benefits
- Simplify the data exchange
- Reduce the reaction time
- Automate the documentation
- Provide more attractive products and services[1]
Traps
- CAM has no value by itself
- Humans need to be involved
- Raw data aren't providing information
- Visual management is required[1]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Marion Purrio and Guido Buchholz (FEF Forschungs- und Entwicklungsgesellschaft Fügetechnik GmbH)Webinar: Vorgehensweise bei Digitalisierungsprojekten in der Schweißtechnik. 29 April 2021.