Data to be processed: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*Workpiece cleanliness | *Workpiece cleanliness | ||
*Room temperature | *Room temperature | ||
*Temperature of the workpieces | |||
*Temperature of the fixture | |||
*Geometry of the set-up | |||
|| | || | ||
*Tensile strength | *Tensile strength | ||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
*Tool position | *Tool position | ||
*Tool forces | *Tool forces | ||
|| || | |||
|- | |||
|| | |||
|colspan="2"| | |colspan="2"| | ||
*Gap between the parts | *Gap between the parts | ||
*Tool wear | *Tool wear | ||
|| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| | || | ||
|colspan="2"| | |colspan="2"| | ||
|| | || | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 29 April 2021
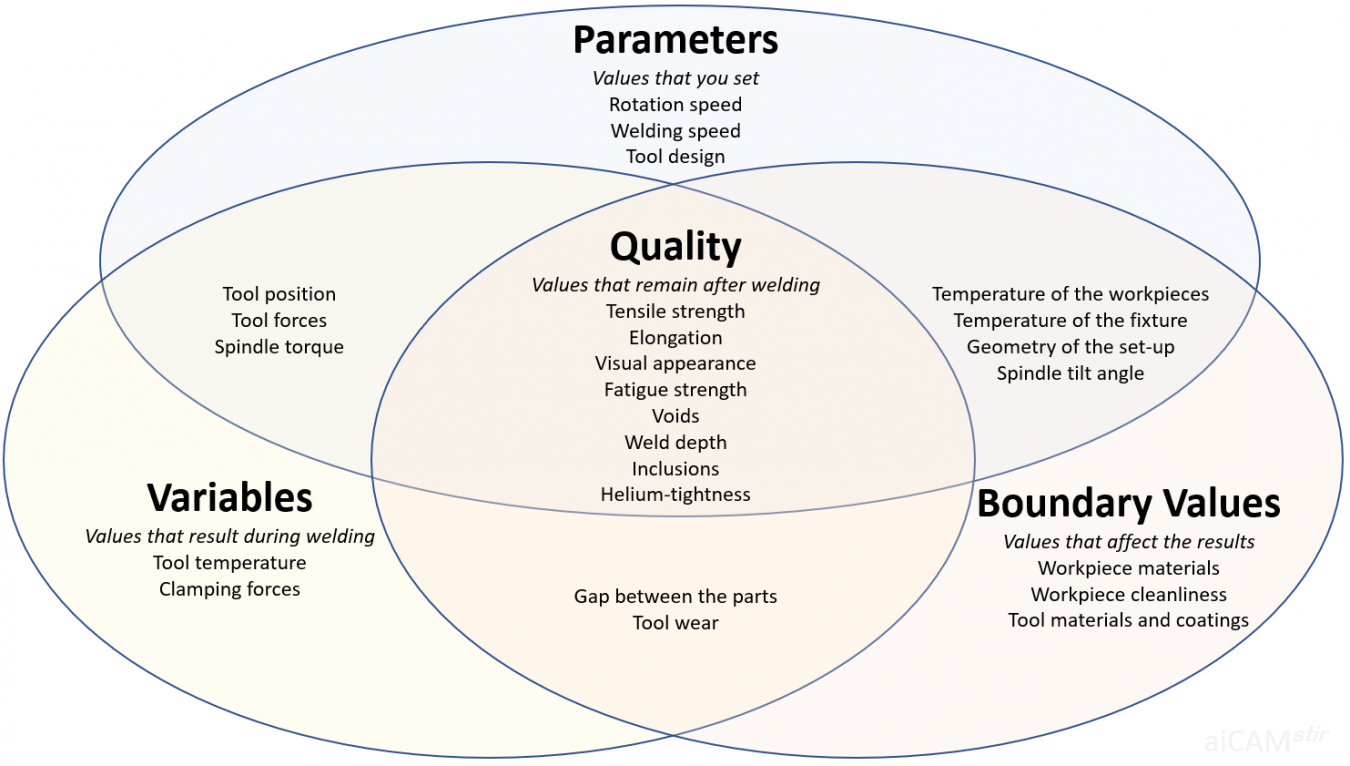
Data to be processed in the aiCAMstir project are parameters, variables, boundary values and quality.
According to digitalisation and data processing experts, the following categorisation of key data could be considered:
| Parameters | Variables | Boundry Values | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Values that you set | Values that result during welding | Values that affect the results | Quality |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|||
The categorisation depends on the concept and complexity of the machine. Modern FSW machines provide close-loop force and position control algorithms, which complicate the distinction between parameters and variables. Some machines use the temperature as a parameter that can be set, e.g. to change the parameters if the tool gets too hot.
Please feel free to improve the classification above or to propose an alternative classification.